Introduction
When it comes to eye health, two conditions that often cause concern are Glaucoma and Cataracts. Understanding the symptoms, differences, and coping strategies for these conditions is crucial for maintaining good eye health and preventing vision loss. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Glaucoma and Cataracts, offering valuable insights and actionable tips.
Glaucoma: Symptoms and Causes
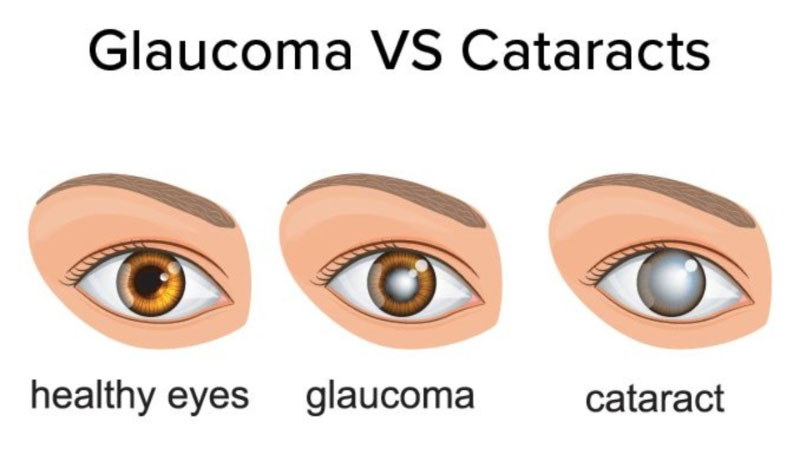
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, often due to elevated pressure within the eye. The most common type, Open-Angle Glaucoma, typically develops slowly and without noticeable symptoms until significant vision loss occurs. On the other hand, Angle-Closure Glaucoma manifests suddenly with severe symptoms like eye pain, headache, nausea, and blurred vision.
The primary cause of Glaucoma is the buildup of fluid (aqueous humor) inside the eye, leading to increased intraocular pressure. Other risk factors include age, family history, ethnicity, and certain medical conditions like diabetes and hypertension.
Cataracts: Symptoms and Causes
Cataracts refer to the clouding of the lens in the eye, leading to blurry vision and eventual vision loss if left untreated. Symptoms of cataracts include cloudy or blurred vision, faded colors, sensitivity to light, and difficulty seeing at night.
The leading cause of cataracts is aging, as the proteins in the eye’s lens break down and clump together over time. However, cataracts can also develop due to factors such as prolonged exposure to UV radiation, smoking, diabetes, and certain medications like corticosteroids.
Key Differences Between Glaucoma and Cataracts
While both Glaucoma and Cataracts can cause vision impairment, they affect the eyes differently and require distinct treatment approaches. Glaucoma primarily damages the optic nerve and is associated with increased intraocular pressure, whereas Cataracts involve the clouding of the eye’s lens.
Furthermore, Glaucoma often progresses slowly and may not present noticeable symptoms until advanced stages, while Cataracts typically cause gradual vision deterioration over time, allowing for early detection and intervention.
Coping Strategies and Treatment Options
Glaucoma Management
Management of Glaucoma aims to lower intraocular pressure to prevent further damage to the optic nerve. Treatment options include:
- Medications: Eye drops or oral medications to reduce intraocular pressure.
- Laser Therapy: Procedures like laser trabeculoplasty to improve drainage of fluid from the eye.
- Surgery: Invasive procedures like trabeculectomy to create a new drainage channel for excess fluid.
Cataract Treatment
The primary treatment for cataracts is surgical removal of the cloudy lens and replacement with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). Cataract surgery is a safe and effective procedure that can significantly improve vision and quality of life for affected individuals.
Conclusion
In summary, Glaucoma and Cataracts are two common eye conditions that can impact vision and quality of life if left untreated. Understanding the symptoms, differences, and available treatment options is essential for early detection and effective management. By prioritizing regular eye exams and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can minimize their risk of developing these conditions and preserve their vision for years to come.






